Extruded polystyrene is a versatile insulation commonly used in building construction. Find out if it’s right for your next project by exploring its thermal performance and putting it toe-to-toe with comparable options.
What is XPS Insulation?
Extruded Polystyrene (abbreviated XPS) is a common insulation building material used in the construction of homes and commercial buildings. It’s the same material used for foam egg cartons, except that it’s extruded into board form when used as insulation.
XPS foam insulation boards come in a variety of sizes, typically 24” x 96” or 48” x 96” and thicknesses ranging from just under 1” to more than 4” thick in some cases.
XPS is used in construction to insulate walls, foundations, and under concrete slabs.
There are six types of XPS classified by varying density levels. Here are the six types of XPS, according to the ASTM C578 standard:
6 Types of XPS Insulation
R-Value Explained
R-value is the measure of how well insulation performs. A higher R-value means that the material is a better insulator, that keeps heat from passing through it. So when used on a building’s envelope, a higher R-value will keep heat out of a building during the summer, and inside the building during the colder months.
R-value is cumulative. That means that a thicker material correspondingly increases your R-value. Theoretically, a two-inch thick insulation board will have double the R-value of a one-inch board of the same material. Contractors can also double up the layers of insulation to achieve a higher R-value. Using multiple layers is advantageous because it allows builders to stagger joints in order to reduce thermal bridging and heat loss at board perimeters.
XPS Insulation R-Value
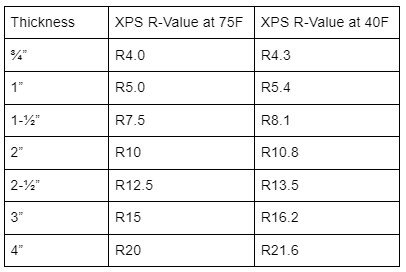
The R-value of XPS rigid insulation sits at R5 per inch. Let’s look at a table that shows xps insulation R-value per inch for Type IV, 25 psi XPS.
XPS Insulation R-Value per Inch
The above comparison of XPS rigid insulation R-values shows a slight difference in performance with different temperatures. XPS actually performs better at 40 degrees Fahrenheit than at 75 degrees. For example, 2-½” XPS insulation has an R12.5 at 75 degrees and jumps up to R13.5 at 40 degrees.
It’s also worth noting that all types of XPS have a similar thermal performance except type XII, which is slightly lower than the other five types.
Comparing XPS Insulation R-Value
The R-value of extruded polystyrene is mediocre when compared XPS to other types of foam board insulation. Here is a head-to-head comparison:
XPS Insulation R-Value Chart Comparison
*Values are for Type I EPS at 75 degrees F.
From the chart above, it’s clear that extruded polystyrene insulation R-values lean toward the higher end of the three options, but remain in the middle between EPS and polyiso.
Polyiso R-Value
Polyiso provides the highest R-value per inch of the three foam board insulation options listed. With R6.0 per inch, you can achieve R15 with just 2-½”, and save half an inch of material if you use XPS (R15 XPS requires 3” thickness). If you’re trying to achieve high thermal performance with a thinner profile, polyiso is a solution to the problem.
Polyiso Benefits
It’s not just the high insulating value per inch that makes polyiso a superior foam insulation choice. There are many benefits to choosing polyiso for your building envelope insulation. Here are some of the reasons to choose polyiso for your next project:
Better fire resistance than XPS
Similar or better moisture resistance than XPS
Tailored facer solutions with polyiso that are not available with XPS
Find the Best Insulation Solution with Rmax
There is no wrong choice for insulation when you’re picking from the right bucket. However, there are good, better, and best solutions. Polyiso is on top as the best performing foam board insulation option on the market for many applications.
Let us help you decide whether it’s right for your next project by reaching out to your local Rmax representative today!