The commercial construction industry demands high performance and efficiency. When it comes to insulation, making the right choice between R13 and R15 can significantly impact your building's energy consumption, comfort levels, and overall sustainability.
In this article, we help you understand the difference between R13 and R15 insulation so that you can make an informed decision considering the specifics of your project.
Picking the Right Insulation
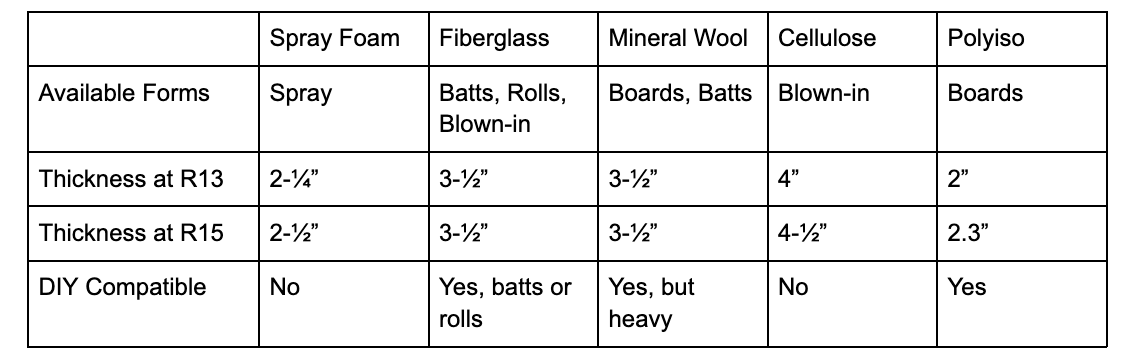
R13 and R15 insulation is available in multiple types. You can get R13 and R15 spray foam, fiberglass, mineral wool, cellulose, polyiso, and more. R13 and R15 insulation can be installed in boards, loose-fill, batts, or rolls. Below, we compare these two insulation options.
R13 vs R15: Insulation Options:
More factors to consider when picking the type of insulation to use include material cost, ease of installation, the need for special equipment, compatibility with meeting building code requirements, and where the insulation will be installed. You may install multiple types of insulation throughout your home depending on your application.
Meeting Code
According to EnergyStar.gov, R13 to R15 is recommended in wall cavities in all climate zones. However, some climate zones may require additional continuous insulation sheathing. For example, in colder climates (Zones 6, 7, and 8), R5 or R6 continuous insulation is required in addition to the cavity R13 or R15. Local energy codes may require even more insulation.
The R-Value Factor
So, what is R-value anyway? R-value is a metric that tells us how well insulation performs at reducing heat loss. When comparing R13 to R15, insulation designated as R15 performs better at reducing heat loss than R13. R-values are generally cumulative, meaning that you can stack two layers of R6 insulation boards to achieve R12. However, in the case of R13 vs. R15 fiberglass and mineral wool batts, it seems they are the same thickness: 3-½”. This is likely due to slight density differences that allow the batts to still fit into the standard wall cavity.
R13 vs. R15 Insulation
R13 and R15 batt insulation is made to fit inside wall cavities. However, other forms like batts or spray will increase in thickness as the R-value goes up. The cost will also increase in a linear fashion, with R15 being slightly more expensive than R13, regardless of the type of insulation you choose.
Applications of R13 and R15 Insulation
R13 and R15 insulation are commonly used in commercial buildings for a variety of applications, including:
Walls
Exterior walls: R13 insulation is often used in exterior walls in moderate climates. It provides a good balance of cost and performance and can help to reduce energy consumption.
Interior Walls
R15 insulation is typically used in interior walls to improve soundproofing and thermal comfort. This is especially important in offices, conference rooms, and other spaces where noise control is critical.
Ceilings
R13 insulation is commonly used in ceilings in moderate climates. It helps to prevent heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, which can improve energy efficiency and comfort. R15 insulation is used in ceilings in colder climates or buildings with high energy usage. It provides additional thermal resistance and can help to reduce energy costs.
Floors
R13 insulation is sometimes used in floors to prevent heat loss and improve comfort, particularly in areas above unconditioned spaces. R15 insulation is typically used in floors in buildings with high energy usage or where soundproofing is important. This can include offices, schools, and hospitals.
Additional Applications
Refrigerated Spaces
R13 and R15 insulation can be used in refrigerated spaces to improve energy efficiency and maintain cold temperatures
Mechanical Rooms
These rooms often house equipment that generates heat, and R13 or R15 insulation can help to prevent heat transfer and improve comfort.
Pipe and Duct Insulation
R13 and R15 insulation can be used to insulate pipes and ducts to prevent heat loss and improve energy efficiency.
The specific type and thickness of insulation used in a commercial building will depend on a variety of factors, including the climate, building type, energy usage, and budget. It is important to consult with a qualified professional to determine the best insulation solution for your specific project.
R13 and R15 Rated Polyiso Board Insulation
Examples of insulation boards include Rmax Thermasheath® and Durasheath®. Thermasheath® achieves R13 with just 2” thick boards and R15 with 2.3” thickness, while Durasheath® achieves R13 in 2.2” and R15 in 2-½”. It is important to know that polyiso requires additional thickness to achieve higher R-values, so when comparing R13 to R15 insulation, thickness increases with R-value.
Perfect Your Project with Rmax Polyiso
For complex commercial buildings, it's crucial to consult with a qualified insulation contractor or energy auditor. They can assess your specific needs, analyze your local building codes, and recommend the most suitable and cost-effective insulation solution for your project.
Ultimately, the best insulation choice for your commercial building depends on a careful assessment of your specific circumstances and priorities. By considering factors like climate, building type, budget, and environmental impact, you can make an informed decision that optimizes both performance and value. Call our experts today to find the best in polyiso insulation for your unique project.